Blood volume is a critical factor in understanding human physiology, especially when comparing males and females. While the average adult male has about 5 liters (10.5 pints) of blood, the average female has approximately 4 liters (8.5 pints). This difference is primarily due to variations in body size, weight, and hormonal influences. Understanding these differences can provide valuable insights into health, medical treatments, and even athletic performance.
In this article, we will explore how blood volume differs between males and females, what factors influence these differences, and why it matters. We’ll also examine the components of blood, how the body regulates its volume, and what happens when there’s a significant loss of blood.
The Composition of Blood
Before diving into the comparison between male and female blood volume, it’s essential to understand what blood is made of. Blood is a complex fluid that consists of several key components:
- Plasma: Makes up about 55% of blood volume. It’s a yellowish liquid that carries nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): Account for about 44% of blood. These cells contain hemoglobin, which binds to oxygen and transports it to tissues.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs) and Platelets: Together make up about 1% of blood. WBCs are part of the immune system, while platelets help with clotting.
Understanding these components helps explain why blood volume varies between individuals and how it affects overall health.
Blood Volume Differences Between Males and Females
As mentioned earlier, the average adult male has more blood than the average adult female. This difference is largely attributed to:
- Body Size and Weight: Males tend to be taller and heavier on average, which means they have more blood vessels and larger organs that require more blood.
- Hormonal Influences: Testosterone promotes the production of red blood cells, contributing to higher blood volume in males.
- Lean Body Mass vs. Fat Tissue: Males generally have more lean muscle mass compared to females, which supports greater blood volume.
For example:
– An adult male who is about 6 feet tall and weighs around 200 pounds may have approximately 5.7 liters of blood.
– An adult female who is about 5 feet 5 inches tall and weighs around 165 pounds may have about 4.3 liters of blood.
These numbers can vary depending on factors like age, health, and lifestyle.
Why Blood Volume Matters
Blood volume is crucial for maintaining proper circulation, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues, and regulating body temperature. A decrease in blood volume can lead to serious health issues, such as:
- Hypovolemic Shock: A life-threatening condition caused by severe blood loss.
- Dehydration: Can reduce plasma volume and affect overall blood flow.
- Anemia: A condition where the body doesn’t have enough red blood cells to carry oxygen effectively.
On the other hand, an increase in blood volume—such as during pregnancy—can also have significant effects on the body. For instance, a woman’s blood volume increases by about 50% during pregnancy to support the growing fetus and placenta.
Measuring Blood Volume
Healthcare professionals use various methods to assess blood volume, including:
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs like low blood pressure, rapid heart rate, or dry mucous membranes.
- Lab Tests: Hemoglobin and hematocrit levels are commonly used to estimate blood volume.
- Specialized Techniques: Such as nuclear medicine analysis or pulmonary artery catheters for more accurate measurements.
These methods help doctors determine if a patient is experiencing blood loss or dehydration and guide appropriate treatment.
What Happens When You Lose Blood?
Losing a significant amount of blood can be dangerous. Here’s how the body responds:
- Class 1 Blood Loss (15% or less): Slight increase in heart rate, no change in blood pressure.
- Class 2 Blood Loss (15–30%): Elevated heart and breathing rates, possible drop in blood pressure.
- Class 3 Blood Loss (30–40%): Major drop in blood pressure, confusion, and decreased mental alertness.
- Class 4 Blood Loss (Over 40%): Severe hypotension, unconsciousness, and potentially fatal.
The body can usually replace small amounts of blood without issue, but large losses require immediate medical attention, such as blood transfusions.
How the Body Regulates Blood Volume
The body has several mechanisms to maintain stable blood volume:
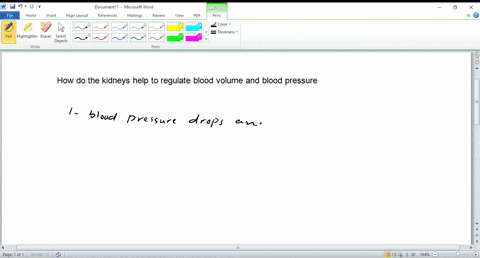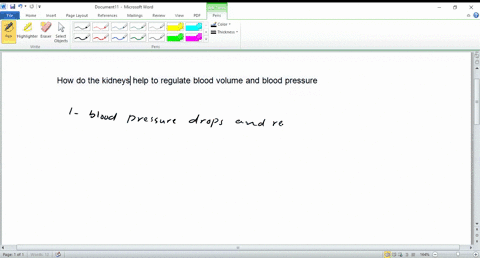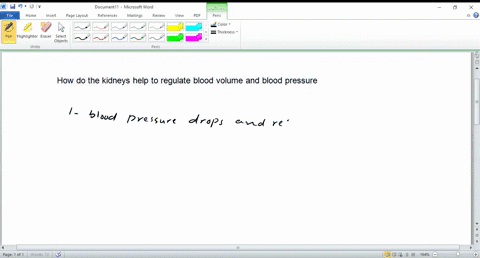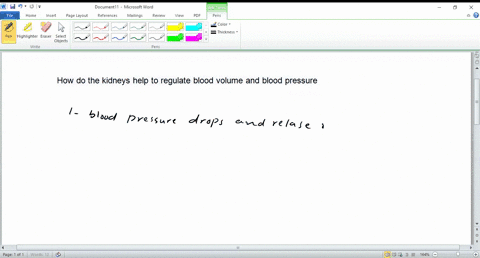
- Kidneys: Help regulate fluid balance by adjusting urine production.
- Hormones: Erythropoietin, for example, signals the bone marrow to produce more red blood cells when needed.
- Bone Marrow: Produces new blood cells to replace those lost due to injury or illness.
However, these processes take time, which is why rapid blood loss may require a transfusion.
Blood Donation and Blood Volume
Blood donation is a common way to help others, but it also highlights the importance of blood volume. A healthy adult can safely donate about 1 pint (500 ml) of blood without experiencing severe side effects. The body typically replaces this volume within a few weeks.
Plasma, which makes up the majority of blood, can be replenished relatively quickly. However, red blood cells take longer to regenerate, which is why there are waiting periods between donations.
Conclusion
In summary, the volume of blood in a female is generally lower than that of a male due to differences in body size, weight, and hormonal factors. Understanding these differences is essential for medical professionals, athletes, and anyone interested in human biology. Whether you’re donating blood, recovering from an injury, or simply curious about your body, knowing how blood volume works can help you make informed decisions about your health.
If you’re interested in learning more about blood donation, medical conditions related to blood volume, or the science behind blood composition, stay tuned for our next articles on US Trending News.
Author Section
Author: Dr. Emily Carter
Title/Role: Medical Writer and Health Analyst
Credentials: Dr. Emily Carter is a medical writer with over 10 years of experience in health journalism and public education. She holds a Master’s degree in Public Health and has contributed to numerous publications on human anatomy and physiology.
Profile Link: Dr. Emily Carter Profile
Sources
- Mayo Clinic – Blood Volume
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention – Blood Donation
- National Institutes of Health – Hematology
Internal Links
Image Placeholder



URL Slug: us-trending-news-blood-volume-male-female
Meta Title: US Trending News: Blood Volume in Males vs. Females
Meta Description: Discover how blood volume differs between males and females, and why it matters for health and medical care. Stay updated with US Trending News.
Featured Snippet: The average adult male has about 5 liters of blood, while the average adult female has around 4 liters. This difference is mainly due to variations in body size, weight, and hormonal influences.











More Stories
What Is Yodo Para Tiroides and How Does It Affect Thyroid Health?
What is WSET? A Comprehensive Guide to Wine Education
US Trending News: What Are Winter Bones? A Guide to the Seasonal Trend in Bone Health