The thyroid gland is a vital organ in the human body, responsible for regulating metabolism, growth, and development. One of the key nutrients required for its proper functioning is iodine, or yodo in Spanish. Understanding what yodo para tiroides means and how it impacts thyroid health is essential for maintaining overall well-being.
The Role of Iodine in Thyroid Function

Iodine is an essential mineral that the body cannot produce on its own, making it necessary to obtain through diet. The thyroid gland uses iodine to synthesize two critical hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones regulate the body’s metabolic rate, influence energy levels, and affect nearly every physiological process.
When the body lacks sufficient iodine, the thyroid may not produce enough of these hormones, leading to hypothyroidism. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include fatigue, weight gain, depression, and sensitivity to cold. On the other hand, excessive iodine intake can also disrupt thyroid function, potentially causing hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid becomes overactive.
Common Sources of Iodine

Incorporating iodine-rich foods into your diet is one of the best ways to support thyroid health. Some of the most effective sources include:
- Seafood: Fish like cod, haddock, and tuna are high in iodine.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese often contain iodine due to the use of iodine-based sanitizers in dairy farming.
- Eggs: Eggs are a good source of iodine, especially the yolk.
- Seaweed and Kelp: These marine plants are naturally rich in iodine.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Certain fruits like strawberries and cranberries, as well as vegetables like potatoes and spinach, contain moderate amounts of iodine.
- Iodized Salt: This is one of the most common dietary sources of iodine worldwide.
Iodine Deficiency and Its Consequences
Iodine deficiency is a significant global health issue, particularly in regions where the soil and water lack sufficient iodine. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), iodine deficiency is the leading cause of preventable mental retardation in children. In adults, it can lead to goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland) and hypothyroidism.
Symptoms of iodine deficiency include:
– Fatigue
– Weight gain
– Dry skin
– Constipation
– Depression
– Goiter
If left untreated, severe iodine deficiency can lead to developmental delays in children and serious health complications in adults.
Iodine Excess and Potential Risks

While iodine is essential, too much can be harmful. Excessive iodine intake can cause hyperthyroidism, which may result in symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, weight loss, anxiety, and heat intolerance. In some cases, it can also trigger or worsen autoimmune thyroid conditions like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease.
It’s important to maintain a balanced intake of iodine, especially if you have a pre-existing thyroid condition. Consulting with a healthcare provider can help determine the right amount of iodine for your specific needs.
Medical Treatments Involving Iodine
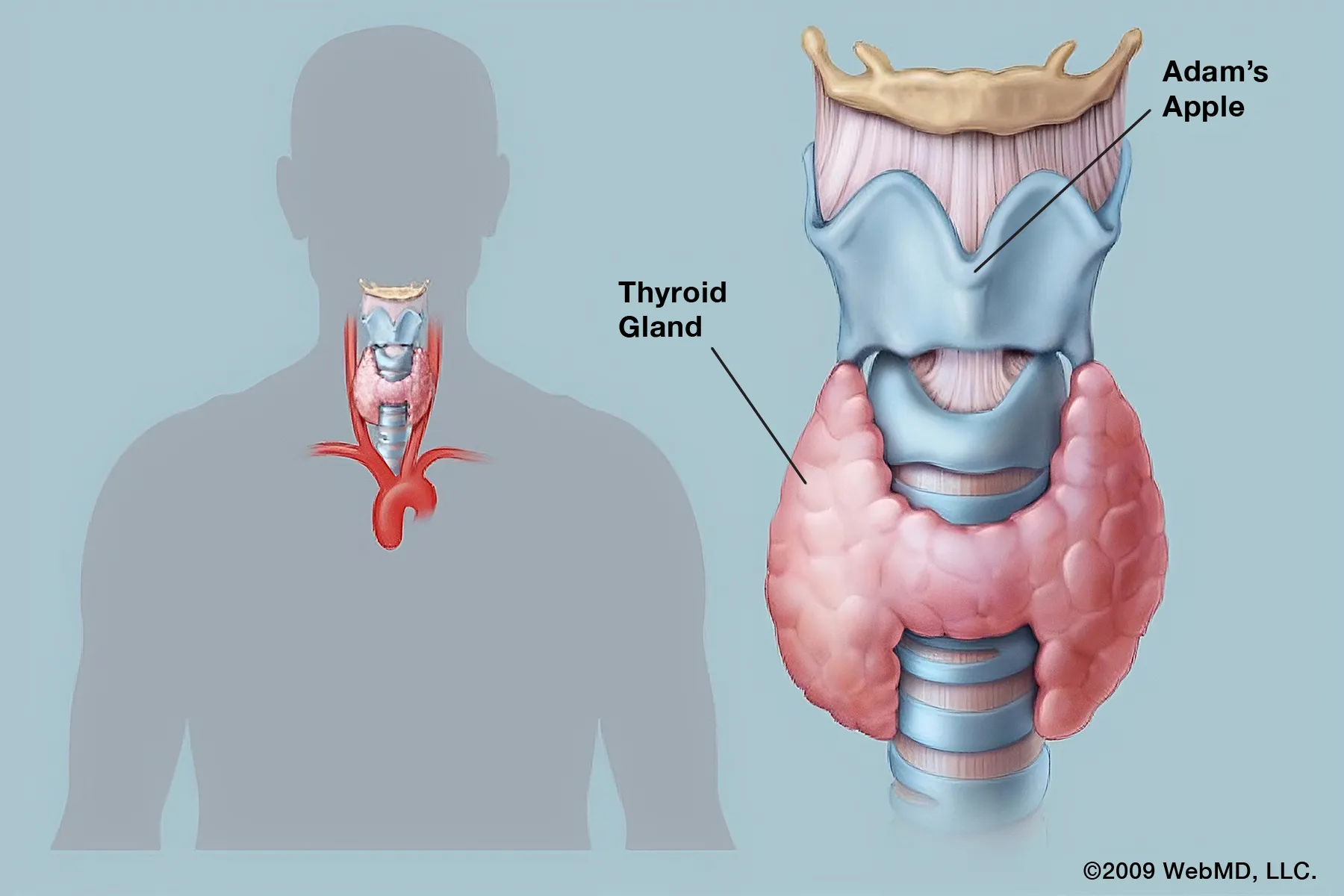
In certain cases, medical treatments involving iodine are used to address thyroid disorders. For example, radioactive iodine (I-131) is commonly used to treat hyperthyroidism and thyroid cancer. This treatment works by targeting and destroying overactive thyroid cells, reducing hormone production.
Patients undergoing this treatment must follow strict safety guidelines to minimize radiation exposure to others. These include avoiding close contact with pregnant women and young children for several days after treatment.
Conclusion
Understanding yodo para tiroides is crucial for maintaining optimal thyroid function and overall health. Iodine plays a vital role in the production of thyroid hormones, and both deficiencies and excesses can lead to serious health issues. Incorporating iodine-rich foods into your diet, monitoring your intake, and consulting with a healthcare professional are all key steps in ensuring proper thyroid function.
Author Section
Author: Dr. Maria Lopez
Title/Role: Endocrinologist and Nutrition Specialist
Credentials: Dr. Lopez is a board-certified endocrinologist with over 15 years of experience in treating thyroid disorders and nutritional deficiencies. She has published numerous articles on thyroid health and has been featured in major health publications.
Profile Link: Dr. Maria Lopez Profile
References
- World Health Organization – Iodine Deficiency
- Mayo Clinic – Thyroid Function and Iodine
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases – Thyroid Disease
Call to Action
Stay informed about thyroid health and the importance of iodine in your diet. Consult with a healthcare professional to ensure you’re getting the right balance of nutrients for optimal well-being. Explore more articles on nutrition and endocrine health to keep your body in top shape.











More Stories
What is WSET? A Comprehensive Guide to Wine Education
US Trending News: What Are Winter Bones? A Guide to the Seasonal Trend in Bone Health
When Is the Next Meteor Shower Tonight? Your Guide to Peak Viewing Times