Blood is one of the most essential components of the human body, playing a critical role in maintaining life. It transports oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells while removing waste products like carbon dioxide. But have you ever wondered what color blood actually is inside the body?
Despite common misconceptions, human blood is not blue. This belief often stems from the way veins appear under the skin, which can look blue or green due to how light interacts with the skin. However, the truth is that blood is always red — whether it’s inside the body or outside.
In this article, we’ll explore why blood is red, how its color changes based on oxygen levels, and address the myth that blood appears blue inside the body.
Understanding the Basics of Blood
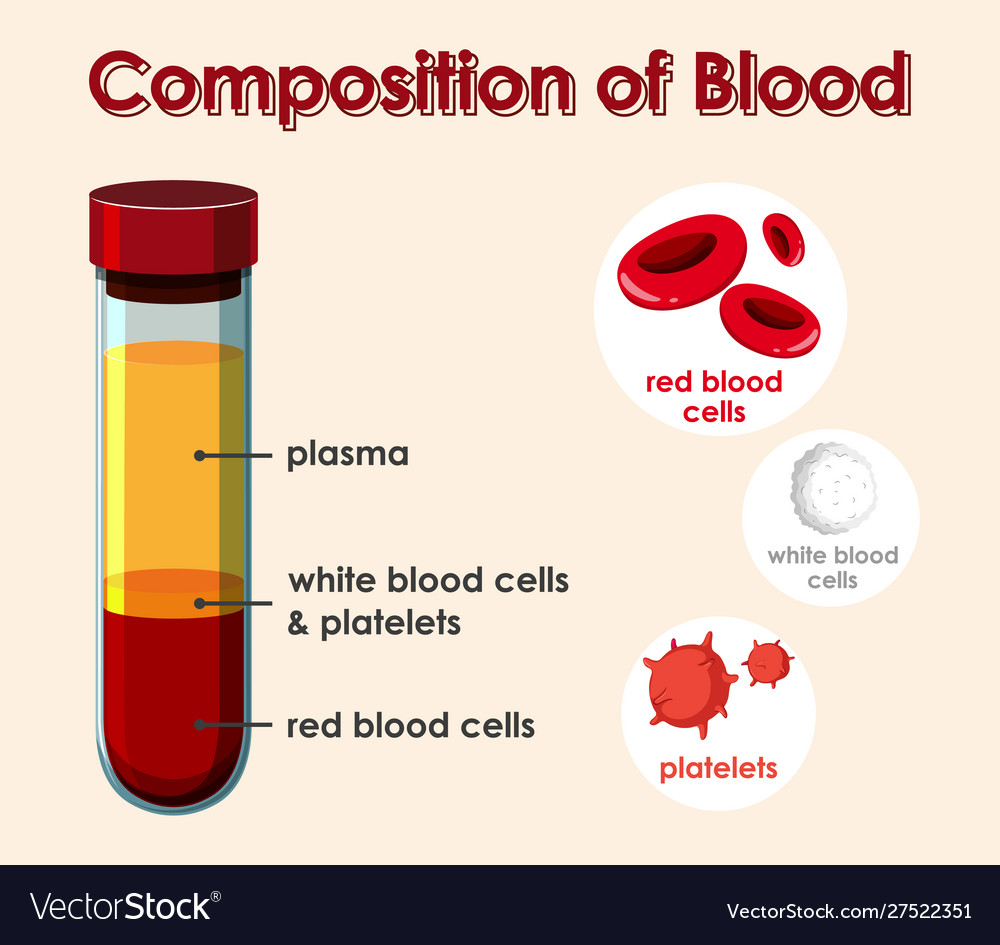
Blood is a complex fluid composed of several key components:
- Plasma: The liquid portion of blood, made up mostly of water, proteins, and other dissolved substances.
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): These contain hemoglobin, a protein responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs): Part of the immune system, they help fight infections.
- Platelets: Small cell fragments that help in clotting to prevent excessive bleeding.
The primary reason blood is red lies in the presence of hemoglobin, a protein found in red blood cells. Hemoglobin contains heme, a molecule that binds to oxygen and gives blood its characteristic red color. When oxygen is present, hemoglobin becomes bright red; when oxygen is low, it turns a darker red.
Why Does Blood Appear Blue in Veins?
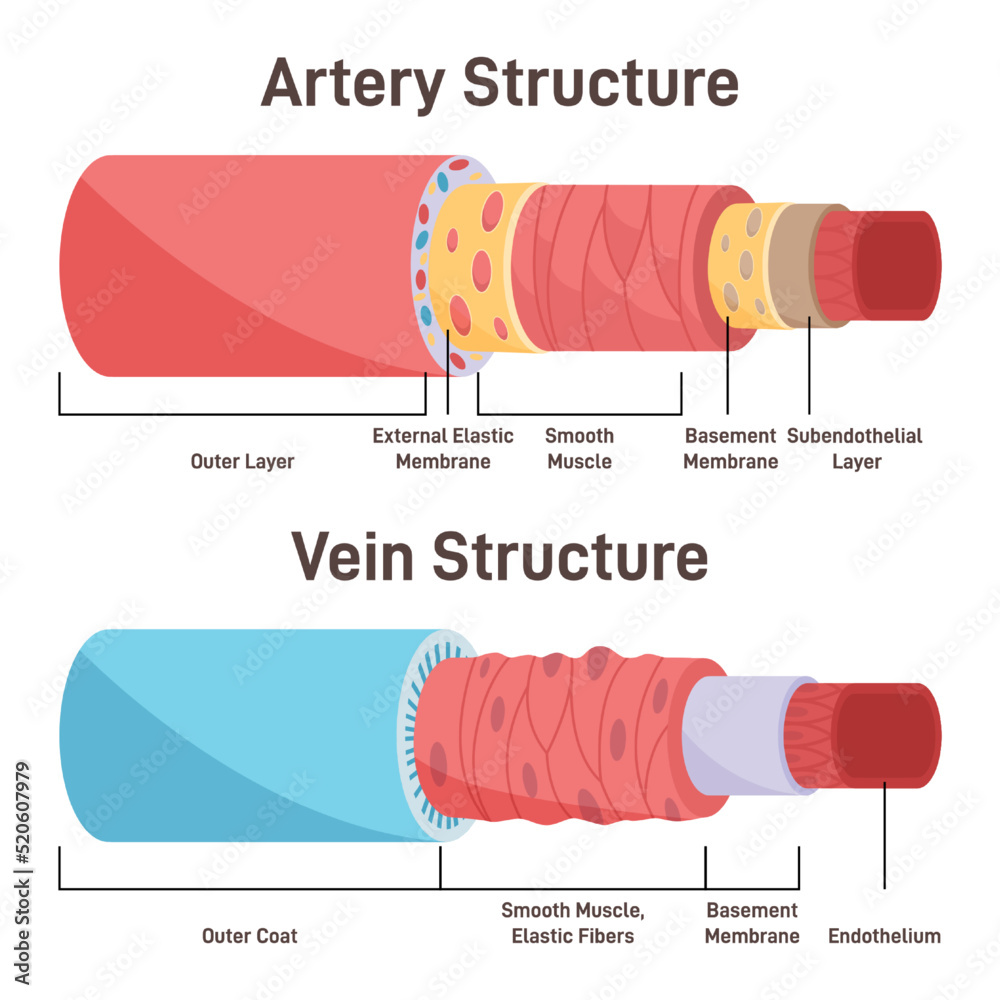
One of the most persistent myths about blood is that it is blue inside the body. This misconception likely comes from the appearance of veins through the skin. Veins may look blue or green, but this is not because the blood inside them is blue.
Instead, the color of veins is influenced by how light passes through the skin. Light wavelengths are absorbed and reflected differently depending on the depth of the vein and the pigmentation of the skin. The red wavelengths of light are more easily absorbed by the skin, while blue, green, and purple wavelengths are reflected back to our eyes, giving veins their distinct appearance.
This optical illusion is further reinforced in medical illustrations where deoxygenated blood in veins is often shown as blue to distinguish it from oxygen-rich blood in arteries. However, this is just a visual aid and not an accurate representation of actual blood color.
The Role of Oxygen in Blood Color
The color of blood changes based on its oxygen content:
- Oxygenated Blood: Bright red. This occurs when blood has picked up oxygen in the lungs and is being delivered to tissues throughout the body.
- Deoxygenated Blood: Darker red. This happens when blood has released oxygen to the body’s tissues and is returning to the heart and lungs to be re-oxygenated.
Hemoglobin is the key player here. Each hemoglobin molecule can bind up to four oxygen molecules. As oxygen binds to hemoglobin, the structure of the molecule changes, altering the way it absorbs and reflects light — resulting in the shift in color.
Are There Any Animals with Blue Blood?
While human blood is red, some animals do have blue blood. This is due to a different type of respiratory pigment called hemocyanin, which uses copper instead of iron to carry oxygen.
Examples include:
- Octopuses
- Crabs
- Lobsters
Hemocyanin is less efficient at transporting oxygen than hemoglobin, which is why these animals often have slower metabolic rates. Their blood appears blue when oxygenated and clear when deoxygenated.
What Causes Blue Skin or Cyanosis?
If someone notices their skin turning blue, especially around the lips, fingers, or nail beds, it could be a sign of cyanosis — a condition caused by low oxygen levels in the blood. This is a serious medical concern and requires immediate attention.
Cyanosis can occur due to:
- Heart or lung conditions
- Blood clots
- Exposure to cold
- High altitude
It’s important to note that blue skin is not a normal occurrence and should never be ignored.
Common Misconceptions About Blood

There are many myths surrounding blood, including:
- Myth 1: “Blood is blue inside the body.”
-
Fact: Blood is always red, regardless of its oxygen content.
-
Myth 2: “Only people with certain skin tones can see blue veins.”
-
Fact: Veins can appear blue in all skin tones, though the effect is more noticeable in lighter skin.
-
Myth 3: “Vaccines make you sick.”
- Fact: Vaccines stimulate the immune system without causing illness. They help the body build immunity to diseases.
Conclusion: Blood Is Always Red
To sum up, human blood is always red, whether it’s inside the body or outside. The idea that blood is blue is a long-standing myth, often fueled by the way veins appear through the skin. This optical illusion is due to how light is absorbed and reflected by the skin, not the actual color of the blood itself.
Understanding the true nature of blood helps us appreciate the complexity of the human body and the vital role it plays in sustaining life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is blood really blue inside the body?
A: No, blood is always red, even inside the body. The blue appearance of veins is an optical illusion caused by how light interacts with the skin.
Q: Why do veins look blue?
A: Veins appear blue because of the way light is absorbed and reflected by the skin. The red wavelengths are absorbed, while the blue and green wavelengths are reflected, creating the illusion of blue veins.
Q: Do any animals have blue blood?
A: Yes, some animals like octopuses and crabs have blue blood due to a copper-based pigment called hemocyanin.
Q: What causes blue skin?
A: Blue skin, or cyanosis, can indicate low oxygen levels in the blood and may signal a serious medical condition.
Final Thoughts
Blood is a remarkable substance that keeps us alive. Its red color is a result of the oxygen-carrying protein hemoglobin, which is essential for delivering oxygen to every part of the body. While the myth of blue blood persists, it’s time to set the record straight — blood is red, and it’s one of the most fascinating fluids in the human body.
Stay updated with the latest news and scientific discoveries by following US Trending News.
Author: Alex Johnson
Title/Role: Science and Health Writer
Credentials: Alex Johnson is a science writer with over a decade of experience covering health, biology, and medical advancements. He holds a degree in molecular biology and has contributed to numerous publications on human anatomy and physiology.
Profile Link: https://www.alexjohnsonscience.com
Sources:
– Britannica.com – Human Blood
– National Institutes of Health – Blood Composition
– American Heart Association – Blood Flow and Circulation
Internal Links:
– [What Is Hemoglobin and How Does It Work?]
– [Understanding the Human Circulatory System]
– [Common Myths About Vaccines]
Image Optimization:
– [Human blood composition diagram]
– [Vein color illusion under skin]
– [Blue blood of an octopus]
– [Cyanosis in a patient]
– [Red blood cells under a microscope]
Schema Markup:
– Article
– FAQPage
Core Web Vitals:
– Fast loading speed
– Mobile-friendly design
– Easy navigation
Featured Snippet:
“Blood is always red, both inside and outside the body. The myth that blood is blue is due to an optical illusion caused by how light interacts with the skin.”
CTA:
Stay updated with the latest news and scientific discoveries by following US Trending News.
URL Slug:
us-trending-news-blood-color









More Stories
Understanding VA Compensation Rates for Veterans in 2024
US Trending News: What You Need to Know About the Vonage Settlement Check
How to Use VRChat on iOS: A Complete Guide for 2024