In the United States, understanding the definition and characteristics of a starling is essential for anyone interested in ornithology, wildlife conservation, or even backyard birdwatching. Starlings are not just common birds—they are a fascinating species with a rich history and unique behaviors that make them stand out among other avian species.
What is a Starling?

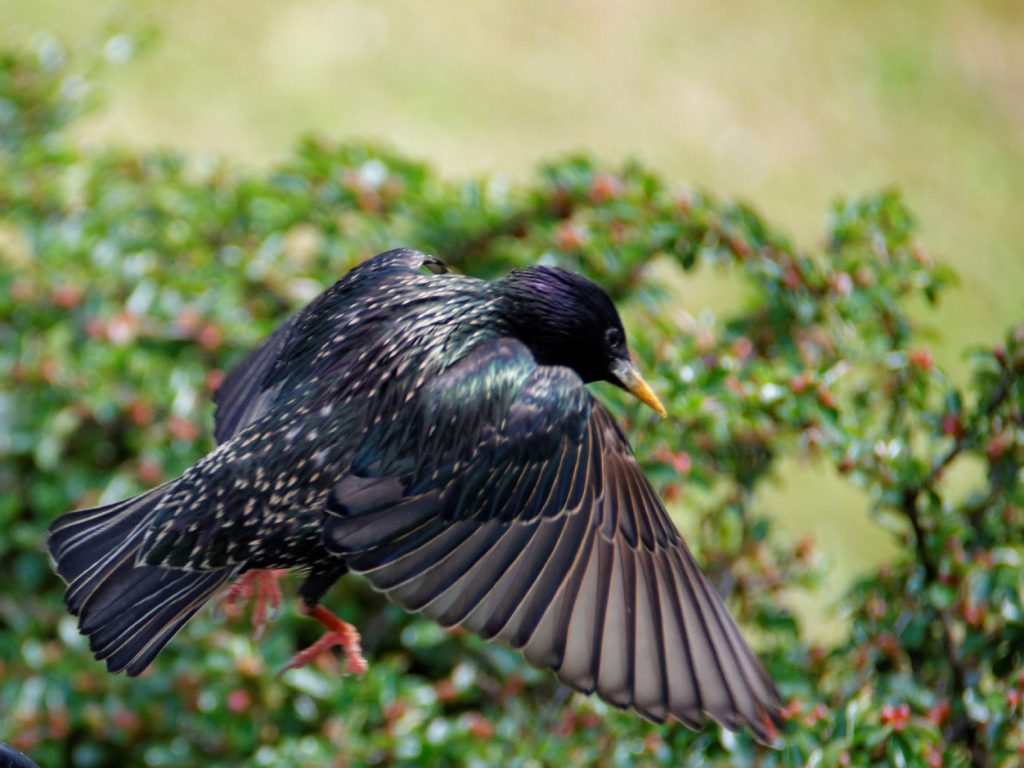
Starlings belong to the family Sturnidae, which includes over 100 species found across various parts of the world. The most well-known species is the common starling (Sturnus vulgaris), also known as the European starling. This bird is approximately 20 cm (8 inches) long, with a stocky build, iridescent black plumage, and a long, sharp bill. While they are native to Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa, they have been introduced to many other regions, including North America.
The introduction of the common starling to the United States was a significant event in the country’s ecological history. It is widely believed that around 80 birds were released in New York City in 1890–91, but recent genetic studies and historical records suggest that the population resulted from multiple introductions in the late 19th century. These birds have since become one of the most abundant bird species in North America.
Key Characteristics of Starlings
Understanding the key characteristics of starlings helps in identifying and appreciating these birds:
- Appearance: Starlings are typically black with iridescent blue or green feathers. Their bills are long and pointed, and their wings are short and rounded.
- Behavior: They are highly social birds, often seen in large flocks called murmurations. These flocks move in synchronized patterns, which can be mesmerizing to watch.
- Diet: Starlings feed on the ground, primarily eating insects, fruits, and seeds. They are also known to consume small vertebrates.
- Vocalizations: Starlings are vocal year-round and are capable of mimicking the sounds of other birds, as well as producing a variety of wheezy and whistling noises.
Starlings in the United States

In the United States, starlings have become an integral part of the ecosystem, although their presence is sometimes controversial. While they play a role in controlling insect populations, they are also considered invasive species because they compete with native birds for nesting sites and food sources.
According to the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, starlings are classified as non-game birds, and licensed hunters are allowed to kill them under certain conditions. This regulation is aimed at managing their population and mitigating their impact on native wildlife.
Despite their reputation as pests, starlings are also admired for their intelligence and adaptability. They are commonly found in urban areas, where they can be seen foraging in lawns, parks, and open fields. In rural settings, they are often spotted perched in groups on trees or flying in tight flocks over fields and roads.
Starlings vs. Other Birds
While starlings share some similarities with other birds, such as crows and blackbirds, there are distinct differences that set them apart:
- Crows: Crows are larger than starlings and have a more varied diet. They are also known for their intelligence and problem-solving abilities.
- Blackbirds: Blackbirds are similar in size to starlings but have a different coloration, with a more uniform black plumage.
- Mourning Doves: Mourning doves are smaller and have a more delicate appearance. They are often seen in pairs and are known for their soft cooing calls.
Ecological Impact of Starlings

The ecological impact of starlings in the United States has been a topic of debate among scientists and conservationists. On one hand, they help control insect populations, which can be beneficial for agriculture. On the other hand, they are known to damage crops, particularly fruits and grains, and displace native bird species by taking over their nesting sites.
In the UK, for example, the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) has noted a decline in the number of starlings visiting gardens, which may indicate changes in their behavior or population dynamics. Similar trends have been observed in other regions, highlighting the need for ongoing research and monitoring.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation efforts aimed at managing starling populations often involve a combination of strategies, including habitat management, public education, and regulated hunting. These efforts are designed to balance the needs of both starlings and native wildlife while minimizing negative impacts on ecosystems.
In addition to these measures, researchers continue to study the behavior and ecology of starlings to better understand their role in the environment. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies and ensuring the long-term survival of both starlings and other native species.
Conclusion
In summary, starlings are a remarkable group of birds with a complex history and a significant presence in the United States. Understanding their definition and characteristics is essential for anyone interested in wildlife, conservation, or simply observing nature. While they are often viewed as pests, their intelligence, adaptability, and unique behaviors make them a fascinating subject of study.
Whether you’re a birdwatcher, a student of biology, or someone who enjoys the natural world, learning about starlings can deepen your appreciation for the diversity of life around us.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Are starlings native to the United States?
A: No, starlings are not native to the United States. They were introduced from Europe in the late 19th century.
Q: Why are starlings considered invasive?
A: Starlings are considered invasive because they compete with native birds for resources and can negatively impact local ecosystems.
Q: Can starlings mimic other birds?
A: Yes, starlings are known for their ability to mimic the sounds of other birds and produce a wide range of vocalizations.
Q: How do starlings behave in the wild?
A: Starlings are highly social birds that often form large flocks. They are active foragers and are known for their distinctive flight patterns.
Additional Resources
For more information on starlings and their impact on the environment, consider visiting the following websites:
- U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service
- Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB)
- National Audubon Society
Stay updated with the latest news and developments in wildlife conservation and environmental science. Explore today’s headlines and discover how they shape our understanding of the natural world.










More Stories
Understanding TEFAP: What You Need to Know About the USDA’s Emergency Food Assistance Program
US Trending News: Everything You Need to Know About Skipjack Tuna: Nutrition, Fishing, and Recipes
What Is the Sacrum? Understanding Its Role and Meaning in the Body