Table of Contents
1. What is Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease?
2. How is CMT Diagnosed?
3. The Role of Genetic Testing in CMT Diagnosis
4. Why Family History Matters in CMT Diagnosis
5. What to Do If Your Diagnosis Is Unclear
6. Finding a CMT Specialist
7. Conclusion
What is Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease?
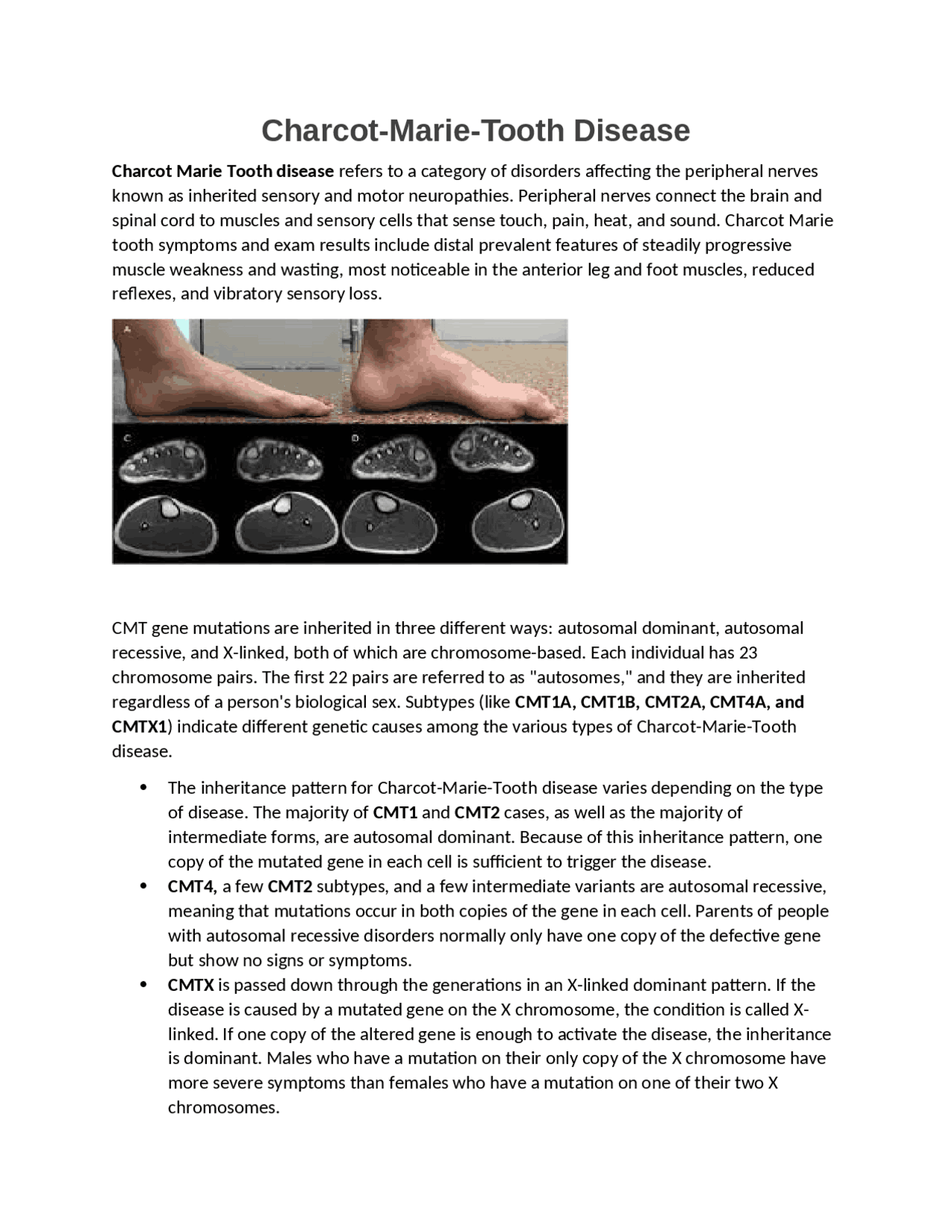
Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease is a group of inherited neurological disorders that affect the peripheral nerves, which are the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. Named after the three doctors who first described it in 1886—Jean-Martin Charcot, Pierre Marie, and Howard Henry Tooth—it is also known as hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy or peroneal muscular atrophy.
CMT affects approximately one in every 2,500 Americans. It is caused by genetic mutations that impact how nerve cells communicate with each other. Over time, these nerves can become damaged, leading to muscle weakness, loss of sensation, and other symptoms. While there is no cure for CMT, various treatments such as physical therapy, braces, and orthopedic devices can help manage its effects.
How is CMT Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease involves a combination of clinical evaluation, nerve conduction studies (NCS), and sometimes genetic testing. Here’s a breakdown of the process:
Clinical Evaluation: Doctors begin by assessing common symptoms such as muscle weakness, foot deformities, balance issues, and numbness or tingling sensations. They also consider family history to identify patterns that may suggest CMT. Other potential causes, like diabetes or vitamin deficiencies, must be ruled out during this stage.
Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS): These tests measure how quickly and effectively nerves transmit signals. Abnormal results can help determine the type of CMT. For example, very slow conduction velocities (<38 m/s) indicate demyelinating CMT (CMT1), while faster conduction velocities (>38 m/s) with reduced amplitudes point to axonal CMT (CMT2).
Genetic Testing: This is used to confirm the diagnosis and identify the specific subtype of CMT. However, it is not always conclusive, as some mutations remain undiscovered or not included in standard testing panels.
Combining these tools allows doctors to ensure an accurate diagnosis while ruling out other potentially treatable conditions. In cases where genetic confirmation isn’t immediately available, a clinical diagnosis based on symptoms, NCS results, and family history is made.
The Role of Genetic Testing in CMT Diagnosis
While genetic testing is not required to diagnose CMT, it plays a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis and identifying the specific subtype. There are over 90 known genetic types of CMT, and each has unique characteristics.
However, it’s important to note that genetic testing does not always provide clear answers. Some mutations may not be detected due to limitations in current testing panels, and not all cases have a known genetic cause. A negative result does not rule out CMT; it simply means the genetic cause was not identified.
Despite this, genetic testing remains valuable because it helps tailor treatment plans and provides insights into the condition’s progression. It also aids in family planning decisions, as CMT is often inherited.
Why Family History Matters in CMT Diagnosis
CMT is a hereditary condition, meaning it often runs in families. Understanding a patient’s family history is an essential part of the diagnostic process. Doctors look for patterns of symptoms such as muscle weakness, balance difficulties, or foot deformities that may suggest an inherited neuropathy.
However, a lack of family history does not rule out CMT. In some cases, the diagnosis may remain unclear even with a strong clinical picture, requiring further testing and monitoring. This highlights the importance of a comprehensive approach to diagnosis, combining clinical evaluation, NCS, and genetic testing when appropriate.
What to Do If Your Diagnosis Is Unclear
In some cases, a definitive diagnosis may not be immediately possible. This can happen if nerve conduction study (NCS) results are inconclusive or if genetic testing does not identify a known mutation. When this occurs, doctors rely on the overall clinical picture, including symptoms, family history, and NCS findings, to make an informed decision.
Specialists at CMTA Centers of Excellence are experienced in managing complex cases and ensuring all potential causes are thoroughly evaluated. If your diagnosis is unclear, your doctor may recommend additional testing or ongoing monitoring to gain more insight.
Finding a CMT Specialist
For individuals seeking a diagnosis or management plan for CMT, finding a specialist is crucial. The CMTA Centers of Excellence are multi-disciplinary clinics dedicated to diagnosing and caring for people with CMT. These centers are staffed by world-renowned physicians, clinicians, and researchers who specialize in CMT and provide comprehensive evaluations and expert guidance.
To find a CMT specialist near you, visit the CMTA Center of Excellence directory. These specialists can help confirm or refine a diagnosis and develop a personalized care plan tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease is a complex genetic disorder that affects the peripheral nerves, leading to muscle weakness, sensory loss, and mobility challenges. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for managing the condition and improving quality of life. The diagnostic process typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, nerve conduction studies, and genetic testing.
While there is no cure for CMT, treatments such as physical therapy, orthopedic devices, and lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms. Understanding the role of family history and the importance of a comprehensive approach to diagnosis is key for those living with or suspecting CMT.
If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms associated with CMT, consult a neurologist or CMT specialist for a thorough evaluation. With the right support and resources, individuals with CMT can lead fulfilling lives.
Meta Title: US Trending News: Charcot Marie Tooth Disease Diagnosis
Meta Description: Learn about the latest in Charcot Marie Tooth Disease diagnosis, including symptoms, testing, and treatment options. Stay updated with the latest news on US health trends.
Author: Dr. Emily Thompson
Title/Role: Neurologist and Medical Writer
Credentials: Board-certified neurologist with over 15 years of experience in diagnosing and treating neurological disorders.
Profile Link: Dr. Emily Thompson Profile
Sources:
– Charcot-Marie-Tooth Association
– Mayo Clinic – Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease
– National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
Internal Links:
– Understanding Neurological Disorders
– Latest in Genetic Research
– Managing Chronic Conditions
Schema Markup:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "Understanding Charcot Marie Tooth Disease Diagnosis: Key Facts and Procedures",
"datePublished": "2025-04-05",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Dr. Emily Thompson"
},
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Health Insight News",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://www.example.com/logo.png"
}
},
"description": "Learn about the latest in Charcot Marie Tooth Disease diagnosis, including symptoms, testing, and treatment options. Stay updated with the latest news on US health trends."
}
Featured Snippet Optimization:
“Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) disease is diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, nerve conduction studies (NCS), and genetic testing. Early diagnosis is essential for effective management.”
Call to Action:
Stay updated with the latest news on Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and other health topics. Explore our articles to learn more about neurological conditions and their diagnosis.
URL Slug:
us-trending-news-charcot-marie-tooth-diagnosis
Image Optimization:
– 
– alt text: “Common symptoms of Charcot Marie Tooth Disease”
– 
– alt text: “Genetic testing for Charcot Marie Tooth Disease”
– alt text: “Finding a specialist for Charcot Marie Tooth Disease”









More Stories
What is an Accord? Understanding the Definition and Usage
US Trending News: What You Need to Know About Alex Smith’s Leg Injury and Recovery
Alex Smith Leg Injury: Updates, Recovery, and Impact on His Career