US Trending News
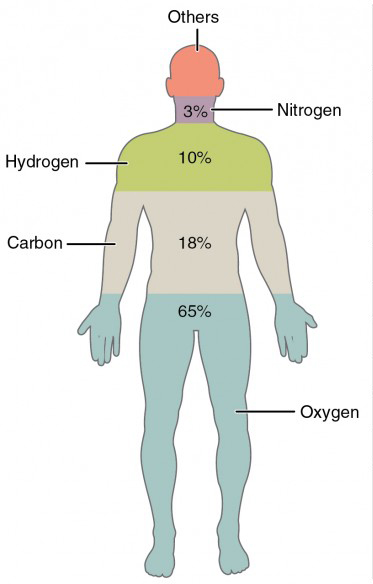
Blood is one of the most essential components of the human body, playing a critical role in transporting oxygen, nutrients, and other vital substances to different parts of the body. But have you ever wondered why blood is red and not blue? This question has puzzled many people, especially children who are curious about how the human body works. In this article, we will explore the science behind why blood is red and not blue, and address some common misconceptions.
The Science Behind Blood Color
The answer to why blood is red lies in a protein called hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells and is responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. It contains iron, which gives it its characteristic red color. When hemoglobin binds with oxygen, it becomes bright red, and when it releases oxygen, it turns into a darker shade of red. This is why arteries, which carry oxygen-rich blood, appear bright red, while veins, which carry deoxygenated blood, appear darker.
But why isn’t blood blue? Some people believe that blood inside the body is blue because of the way veins look through the skin. However, this is a common misconception. Veins may appear blue or green due to the way light interacts with the skin and the depth of the vein. The actual color of blood is always red, whether it’s inside or outside the body.
What Is Hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is a complex protein made up of four polypeptide chains (α1, α2, β1, and β2). Each chain is attached to a heme group, which consists of a porphyrin ring and an iron atom. The iron atom is crucial because it allows hemoglobin to bind with oxygen molecules. This reversible binding of oxygen is what makes hemoglobin so effective at transporting oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body.
When oxygen binds to hemoglobin, it forms a compound called oxyhemoglobin, which is bright red. Once the oxygen is delivered to the tissues, hemoglobin becomes deoxyhemoglobin, which has a darker, purplish-blue appearance. However, even in this state, the blood is still red, just less vibrant.
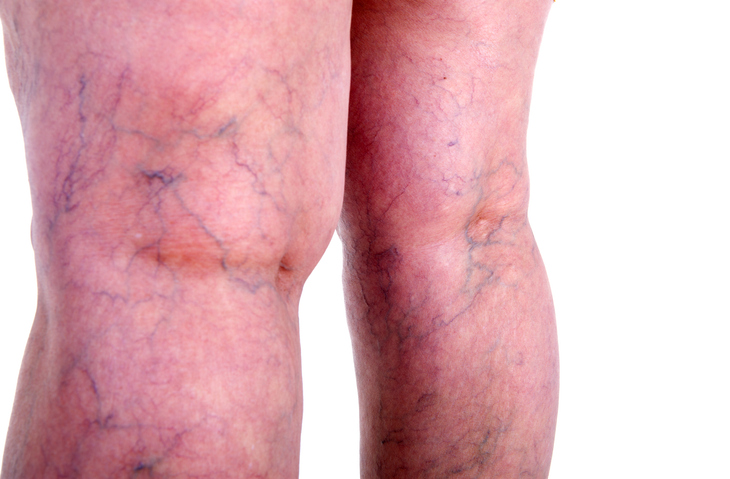
Why Do Veins Appear Blue?
One of the most confusing aspects of blood color is why veins appear blue through the skin. This is due to the way light is absorbed and reflected by the skin and underlying tissue. Light with longer wavelengths (like red) is absorbed more easily by the skin, while shorter wavelengths (like blue and green) are reflected back to our eyes. This is why veins, which are deeper under the skin, can appear blue or green, even though the blood inside them is still red.
This phenomenon also explains why bruises or hematomas (collections of blood under the skin) can appear blue or purple. The color change is not because the blood itself is blue, but because of how light passes through the skin and the surrounding tissue.
Are There Animals With Blue Blood?
While human blood is red, some animals have different colored blood due to variations in their oxygen-carrying proteins. For example:
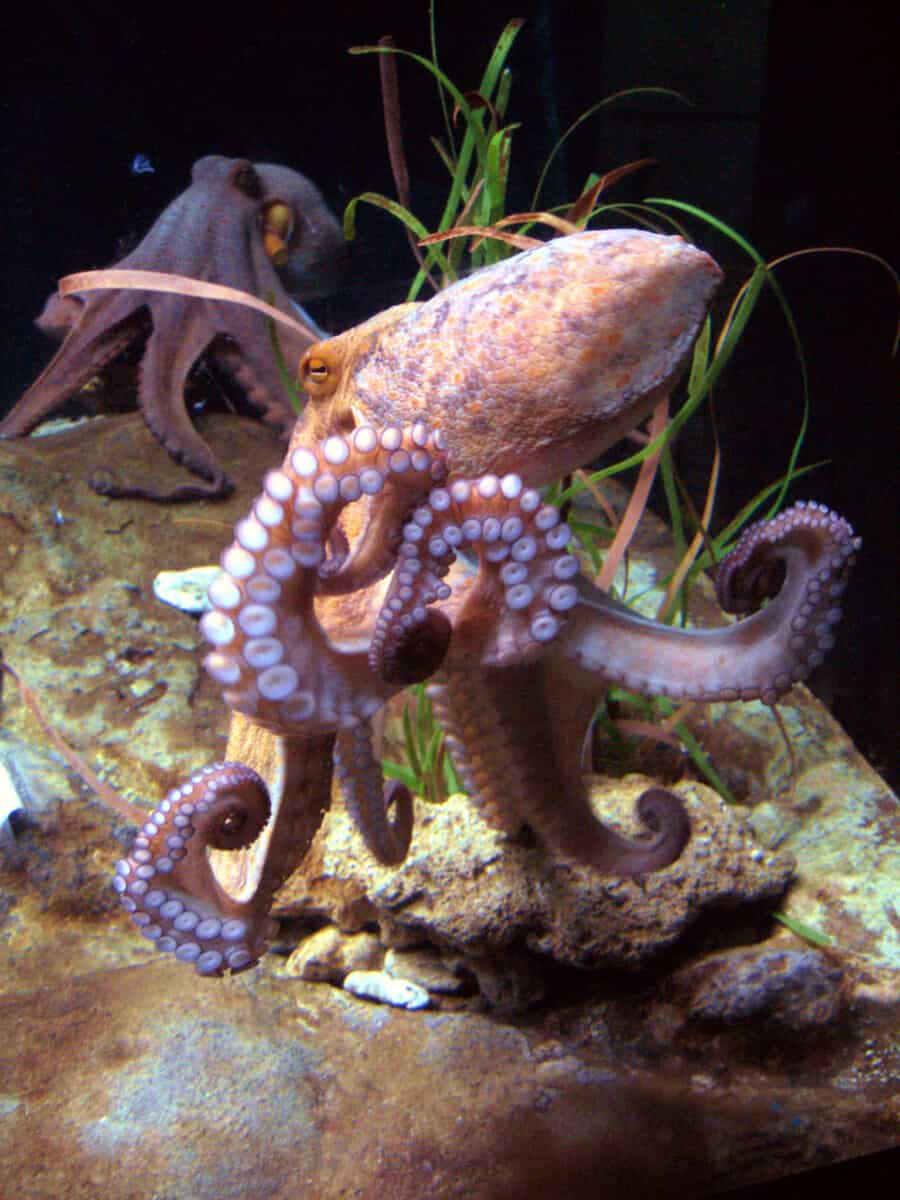
- Octopuses have blue blood because they use a copper-based protein called hemocyanin instead of hemoglobin.
- Lizards can have green blood due to a different type of pigment.
- Insects often have colorless or yellowish blood, as they don’t rely on hemoglobin for oxygen transport.
These differences in blood color highlight the diversity of life and the various ways organisms have evolved to survive in different environments.
Common Misconceptions About Blood Color
Despite the scientific explanation, there are still many myths and misconceptions about blood color. Here are a few of the most common ones:
1. “Blood Inside the Body Is Blue”
This is one of the most widespread misconceptions. While veins may appear blue through the skin, the actual color of blood is always red. Even in the deepest parts of the body, blood remains red.
2. “Only Oxygen-Rich Blood Is Red”
This is partially true. Oxygen-rich blood (found in arteries) is bright red, while oxygen-poor blood (found in veins) is darker. However, both are still red, not blue.
3. “Blue Skin Means Blue Blood”
If someone’s skin appears blue, especially around the lips, nails, or fingertips, it could be a sign of a serious medical condition called cyanosis. This occurs when there is not enough oxygen in the blood, and it is not related to the actual color of the blood itself.
The Role of Hemoglobin in Health
Hemoglobin is not only important for giving blood its red color—it also plays a vital role in maintaining overall health. Without hemoglobin, our bodies would not be able to deliver enough oxygen to our cells, leading to fatigue, dizziness, and even organ failure.
There are also conditions that affect hemoglobin, such as:
- Anemia: A condition where the body doesn’t have enough red blood cells or hemoglobin, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Sickle Cell Anemia: A genetic disorder where hemoglobin causes red blood cells to become crescent-shaped, leading to pain and other complications.
- Thalassemia: Another genetic disorder that affects the production of hemoglobin.
These conditions highlight the importance of hemoglobin in keeping us healthy and functioning properly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, blood is red because of the presence of hemoglobin, a protein that carries oxygen throughout the body. While some people may think blood is blue due to the way veins appear through the skin, this is a visual illusion caused by the way light interacts with the skin. Human blood is always red, whether it’s inside or outside the body.
Understanding the science behind blood color helps us appreciate the complexity of the human body and the vital role that hemoglobin plays in our health. So next time you see a vein or a bruise, remember that the color you see is just an illusion—your blood is still red, and that’s what keeps you alive.

Meta Title: Why Is Blood Red and Not Blue?
Meta Description: Discover the science behind why blood is red and not blue, and learn about hemoglobin’s role in oxygen transport.
Call to Action: Stay updated with the latest science and health news. Explore today’s headlines and learn more about the human body.
Author: Sarah Mitchell
Title/Role: Science Writer and Content Specialist
Credentials: B.S. in Biology, 5+ years of experience writing about health, science, and medical topics.
Profile Link: https://www.sarahmitchellscience.com
Sources:
– The Conversation – Why Is Blood Red?
– Britannica – Hemoglobin
– Mayo Clinic – Cyanosis
Internal Links:
– How the Human Body Works
– The Importance of Oxygen in the Body
– Common Myths About Blood
Schema Markup:
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "Why Is Blood Red and Not Blue in Your Body?",
"description": "Discover the science behind why blood is red and not blue, and learn about hemoglobin's role in oxygen transport.",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Sarah Mitchell"
},
"datePublished": "2025-04-05"
}
Featured Snippet:
“Blood is red because of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Hemoglobin contains iron, which gives blood its red color. Even though veins may appear blue through the skin, the actual color of blood is always red.”











More Stories
67 Emote Clash Royale Emote: Complete List and Guide
What Is the 504 Gateway Timeout Error and How to Fix It?
US Trending News: 67 Emote Clash Royale QR Code: How to Use and Where to Find It