In recent years, job cuts have become a significant concern for both employees and businesses across the United States. As companies navigate economic uncertainties, technological advancements, and shifting market demands, the decision to reduce workforce sizes has become increasingly common. This article explores the multifaceted impact of job cuts, examining how they affect individuals, organizations, and the broader economy.
The Rise of Job Cuts in the Modern Economy
The 2025 US Jobs Report revealed a stark reality: over 800,000 jobs have been lost so far this year, with July alone seeing 62,000 layoffs. This marks one of the worst job growth periods since the pandemic recovery. While government downsizing and AI-driven automation are major contributors, the ripple effects extend far beyond these sectors.
Companies like Microsoft, Intel, and Amazon have made headlines for their large-scale layoffs, often citing cost-cutting measures and strategic realignments. These decisions are not always driven by financial distress but can be part of broader efforts to remain competitive in an evolving landscape. For instance, tech giants are leveraging AI to automate roles, leading to significant reductions in middle management and entry-level positions.
The Human Cost of Job Cuts
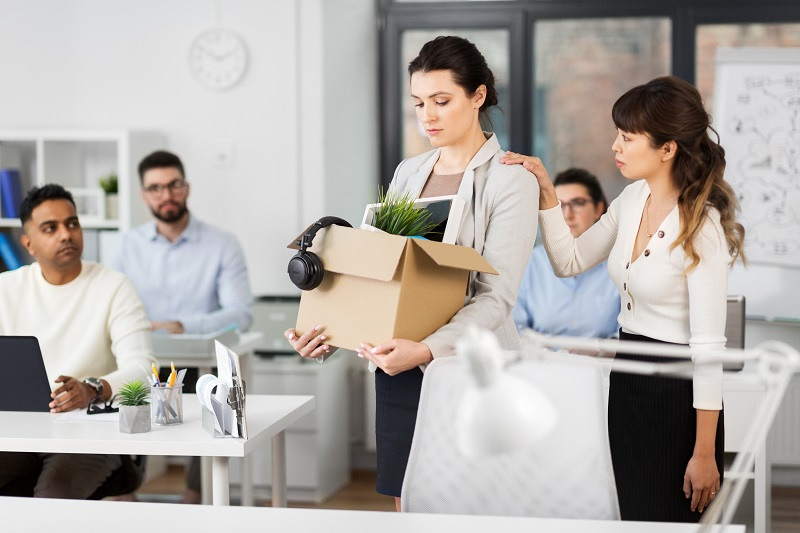

For employees, job cuts represent more than just the loss of income; they can lead to profound psychological and emotional impacts. According to research, survivors of layoffs often experience stress, anxiety, and a decline in morale. The “denial,” “anger,” “fear,” and “acceptance” stages of being laid off, as outlined by Aamodt (2014), highlight the complex emotional journey many face.
Moreover, the long-term consequences of unemployment can be severe. Prolonged joblessness may lead to financial instability, health issues, and a sense of hopelessness. The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that unemployment can last up to six months or longer, exacerbating the challenges faced by those who lose their jobs.
The Business Perspective

From a business standpoint, job cuts are often seen as a necessary evil to maintain profitability and competitiveness. Companies like General Motors and Target have implemented layoffs as part of broader restructuring efforts. These moves aim to streamline operations, reduce costs, and focus on core competencies.
However, the decision to cut jobs is not without risks. Layoffs can damage employee morale, disrupt workflows, and harm a company’s reputation. Additionally, legal and ethical considerations must be addressed, as companies must ensure that layoffs are conducted fairly and transparently.
HR departments play a crucial role in managing the fallout from job cuts. They are responsible for ensuring that layoffs comply with employment laws, communicating effectively with affected employees, and supporting those who remain. As noted by the University of Washington (2018), HR professionals must be heavily involved in every stage of the layoff process, from planning to implementation.
The Role of Technology and Automation

The integration of artificial intelligence and automation has significantly influenced the job market. Companies are increasingly adopting AI to enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs. For example, Microsoft and Intel have both announced substantial job cuts due to their focus on AI development.
While these advancements offer benefits such as increased productivity and innovation, they also pose challenges for workers whose roles are at risk of being automated. The shift towards AI-driven operations requires employees to acquire new skills and adapt to changing job requirements.
Political and Economic Implications
Job cuts have become a hot topic in political discourse, with differing perspectives on their causes and consequences. Conservative media often frames layoffs as a necessary step to reduce bureaucracy and improve efficiency, while liberal media tends to view them as a sign of economic instability.
The 2025 US Jobs Report has sparked debates about the state of the economy and the effectiveness of current policies. Analysts suggest that the weak job growth data indicates underlying economic strains, prompting calls for policy changes to support workers and stimulate job creation.
Sector-Specific Challenges
Certain industries have been hit harder by job cuts than others. Manufacturing, construction, and retail have all experienced significant declines in employment. For instance, manufacturing shed 11,000 jobs in July alone, while construction gained only 2,000 jobs due to stricter immigration enforcement and rising labor costs.
These sector-specific challenges highlight the need for targeted interventions to support workers and stabilize the economy. Governments and businesses must collaborate to address the unique needs of different industries and promote sustainable job growth.
The Path Forward
As the job market continues to evolve, it is essential for both employees and employers to adapt. Workers should focus on building skills that are less likely to be automated, diversifying income streams, and maintaining a strong safety net. Employers, on the other hand, must prioritize transparency, fairness, and support during times of change.
In conclusion, job cuts are a complex issue with far-reaching implications. While they can provide short-term benefits for businesses, the long-term consequences for employees and the economy are significant. By understanding the factors driving job cuts and implementing effective strategies to mitigate their impact, we can work towards a more resilient and equitable job market.
FAQ – Understanding Job Cuts
Q1: What is the impact of job cuts on employees?
Job cuts can lead to financial instability, stress, and a decline in morale. Survivors of layoffs often experience emotional challenges, including anxiety and a sense of insecurity.
Q2: How do companies decide which employees to lay off?
Companies typically consider factors such as performance, seniority, and the strategic needs of the organization. HR departments play a critical role in ensuring that layoffs are conducted fairly and transparently.
Q3: What are the long-term effects of job cuts on the economy?
Prolonged job cuts can lead to higher unemployment rates, reduced consumer spending, and decreased economic growth. They can also exacerbate social inequalities and create a sense of uncertainty among workers.
Q4: How can employees prepare for potential job cuts?
Employees should focus on developing transferable skills, maintaining a strong professional network, and building an emergency fund. Staying informed about industry trends and seeking continuous learning opportunities can also help in navigating a changing job market.
Author Section
Author: WYATTE GRANTHAM-PHILIPS
Title/Role: Senior Correspondent, Associated Press
Credentials: With over a decade of experience covering economic and labor issues, WYATTE GRANTHAM-PHILIPS has provided in-depth reporting on the impact of job cuts on workers and businesses. His work has been featured in major publications and has influenced policy discussions at the national level.
Profile Link: LinkedIn Profile
Trust & Credibility
Call to Action
Stay updated with the latest news and insights on job cuts and their impact on the U.S. economy. Explore today’s headlines to understand the evolving job market and make informed decisions for your career and business.










More Stories
Understanding Rombauer: A Comprehensive Guide to the Iconic Wine Brand
US Trending News: What Is Sarah Oil and Why Is It Trending Now?
What is a Shaft? Understanding the Definition and Uses in Engineering and Mechanics